RBI Guidelines 2025: Minor Account or Guardian-Operated Account – Which is Better?
This long-form guide explains the difference between a guardian-operated account and a self-operated minor account in India. It answers why the rules changed recently, what each account allows, the risks and benefits, how banks implement the rules, and what is the rbi guidelines for minors, KYC and documentation required for minor and guardian operated account, and a practical 10-point checklist you can copy and paste. If you want short explainers or printable checklists, visit our Blog https://ourfinocracy.com/blog/ or contact us at https://ourfinocracy.com/contact/.
Table of Contents
Why this matters now
RBI updated and clarified norms affecting minor accounts in 2025. The key change allowing minors aged 10 and above to open and operate savings and term deposit accounts independently (subject to bank-set limits and KYC) makes this a timely topic for parents, guardians, teachers and financial planners. These changes aim to increase financial inclusion while balancing risk controls and transition procedures at majority (age 18). Business Standard
Executive summary of the rules and practical implications
Difference between guardian operated and minor savings account India
- Minors of any age may have a bank account opened in their name by a natural or legally appointed guardian. The mother can be a guardian and should be accepted as such by banks in line with earlier RBI direction.
- Minors aged 10 years and above may be allowed by banks to open and operate savings or term deposit accounts independently, with appropriate limits set by the bank as per its risk policy. This is not an automatic universal right; each bank defines exact limits and facilities.
- Guardian-operated accounts remain valid for all ages; they are used when a parent or guardian prefers control and oversight. A guardian-operated account is typically required for younger children and where parents prefer to retain transaction control. Ujjivan Small Finance Bank
- Upon turning 18, minors must provide fresh KYC, signatures and any other documentation the bank requires to convert the minor account into a regular adult account. The Economic Times
Deep detail 1
Definitions and legal basis
Guardian-operated account means the deposit account of a minor opened and operated by the child’s natural or legally appointed guardian. The RBI circular from 1976 has long permitted mothers to act as guardians; recent RBI restatements in 2025 have reiterated and clarified the practice to align with financial inclusion objectives. The Master Direction and subsequent circulars describe the operational framework banks must follow for opening and operating accounts of minors. Reserve Bank of India
Self-operated minor account means an account opened by a minor aged 10 years or older who can operate the account independently subject to limits and risk controls the bank sets. The bank is allowed to impose transaction limits, restrict facilities like withdrawals above a limit, and define online banking or card privileges depending on its internal policy and risk appetite.
Deep detail 2
Practical differences in account operation and facilities
- Signatories and control
Guardian-operated account: Guardian signs and operates the account on behalf of the minor. The guardian can add or remove services, set debit instruments, and receive account statements.
Self-operated account 10+: The minor uses their own signature (or prescribed acceptance) and can transact within bank-set limits. Guardian involvement may be limited to opening and consent. - Debit cards, ATM and internet banking
Banks may or may not provide ATM/debit cards and internet banking for minor accounts. For self-operated accounts, banks typically allow limited access to these facilities within prescribed transaction caps and after risk assessment. For guardian-operated accounts the guardian chooses which facilities to enable. Ujjivan Small Finance BankIIBF - Cheques and overdraft
Most banks do not allow minors to have cheque books or overdraft facilities by default. Where facilities are offered, banks will subject them to strict limits and approvals. RBI guidance generally discourages overdraft facility for minor accounts. Reserve Bank of India
Deep detail 3
KYC, documentation and identification
KYC is mandatory for all accounts. For minors:
• Guardian-operated account: guardian KYC plus minor’s basic details and birth proof are required.
• Self-operated account: the minor must satisfy KYC as per bank policy; acceptable documents can include Aadhaar, school ID, birth certificate, passport, etc. Banks will follow RBI’s KYC Master Direction and FAQs for verification and re-KYC processes. Recent RBI communications emphasize ease of re-KYC for dormant/inoperative accounts while ensuring compliance. Reserve Bank of India
Deep detail 4
Limits, risk management and bank discretion
Allowing 10+ minors to operate accounts independently is balanced by bank discretion to set transaction and facility limits. Banks will assess fraud risk, geographies, account usage patterns and may restrict high risk channels (e.g., large outward transfers, high-value cards, cheque books). This preserves protection for minors and reduces the bank’s operational and compliance risk. Banks may set different daily/monthly caps and impose velocity checks.
Deep detail 5
Teaching financial literacy while ensuring safety
If you allow a minor to operate an account:
• Start with small, restricted capabilities such as viewing balance, small-value transfers, or a restricted debit card with low cap.
• Use guardian alerts and SMS statements so parents can monitor.
• Teach the child basics of UPI safety, PIN secrecy, and to avoid sharing OTPs. Tools such as NPCI’s UPI Circle (delegated payments) can be helpful when the guardian wants to allow spending from the parent’s account without sharing PINs. NPCIThe Economic Times
Deep detail 6
Transition to adulthood and continuity planning
Rbi guidelines for minor bank account transition at 18
When a minor becomes 18:
• Banks require fresh KYC and the minor’s signatures to continue the account as an adult account.
• Any guardian authority ends; rights pass fully to the account holder.
• It is a best practice to notify the bank in advance and confirm the documentation required to avoid account freezes or operational interruptions. The Economic Times
Minor Account vs Guardian-Operated i.e. self operated minor bank account age 10 india checklist

Guardian operated savings account benefits and risks
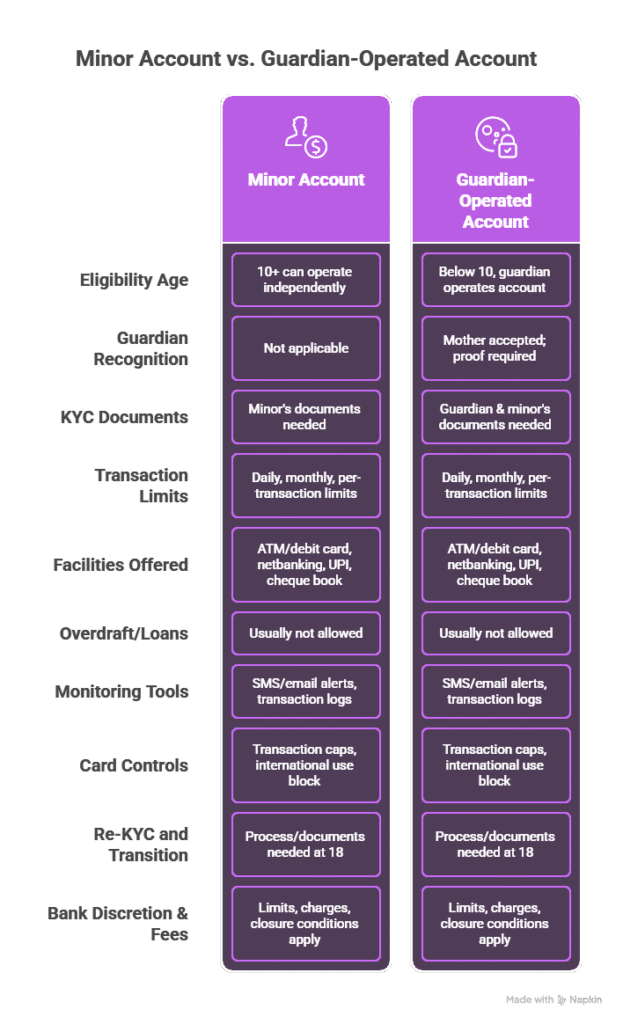
Eligibility Age: Confirm whether the minor is below 10, between 10 and 18, or 18 and above and if the bank allows independent operation for 10+.
Guardian Recognition: Check if the bank accepts mother as guardian and what proof is required.
KYC Documents: List required documents for the guardian and the minor including Aadhaar, birth certificate, school ID, passport, PAN if any.
Transaction Limits: Ask the bank for daily, monthly and per-transaction limits for the minor account.
Facilities Offered: Confirm availability of ATM/debit card, netbanking, UPI, cheque book, and mobile alerts.
Overdraft/Loans: Verify whether overdraft or other credit facilities are allowed (usually not).
Monitoring Tools: Check if guardian can receive SMS/email alerts and view transaction logs.
Card Controls: If a card is issued, check for transaction caps, international use block, and online merchant controls.
Re-KYC and Transition: Note the process and documents needed when the minor turns 18.
Bank Discretion & Fees: Clarify bank’s right to set/modify limits, charges for services, and closure conditions.
How to use this checklist
Use it when you visit the bank or compare bank product pages online. For quick calculators and planning help to estimate allowance, tax implications or future value of savings, use our Best & Smart Financial Calculator https://ourfinocracy.com/calculators/. For professional help or family finance services see https://ourfinocracy.com/services/ and to learn more about our approach visit https://ourfinocracy.com/about-us/. If you need help writing bank letters or documentation templates, contact us at https://ourfinocracy.com/contact/.
Practical examples and recommended setups
For ages 5–9: Open guardian-operated account; enable viewing rights and monthly statement emails; no card or netbanking.
For ages 10–14: Consider self-operated account if the child is mature; allow UPI with strict limits or a restricted debit card with daily cap.
For ages 15–17: Gradually increase access; allow limited netbanking with two-factor authentication, but keep high-value transfers blocked.
For transitions at 18: Have a checklist ready for fresh KYC, address proof, PAN and signature updates.
Q. Is it safe to give a debit card to my 12-year-old?
A. Only if the bank allows a restricted card with low caps, alerts to guardian and merchant controls.
Q. Can I remove guardian access once the child is 10?
A. That depends on the bank and the account type. If the child opens a self-operated account at 10+ banks may allow the child to operate independently subject to limits. Always confirm with the bank.
Q. What happens to joint gifts and deposits at 18?
A. Gifts remain in the account and transition to the account holder. Keep a record of gifted amounts for tax and clarity.












