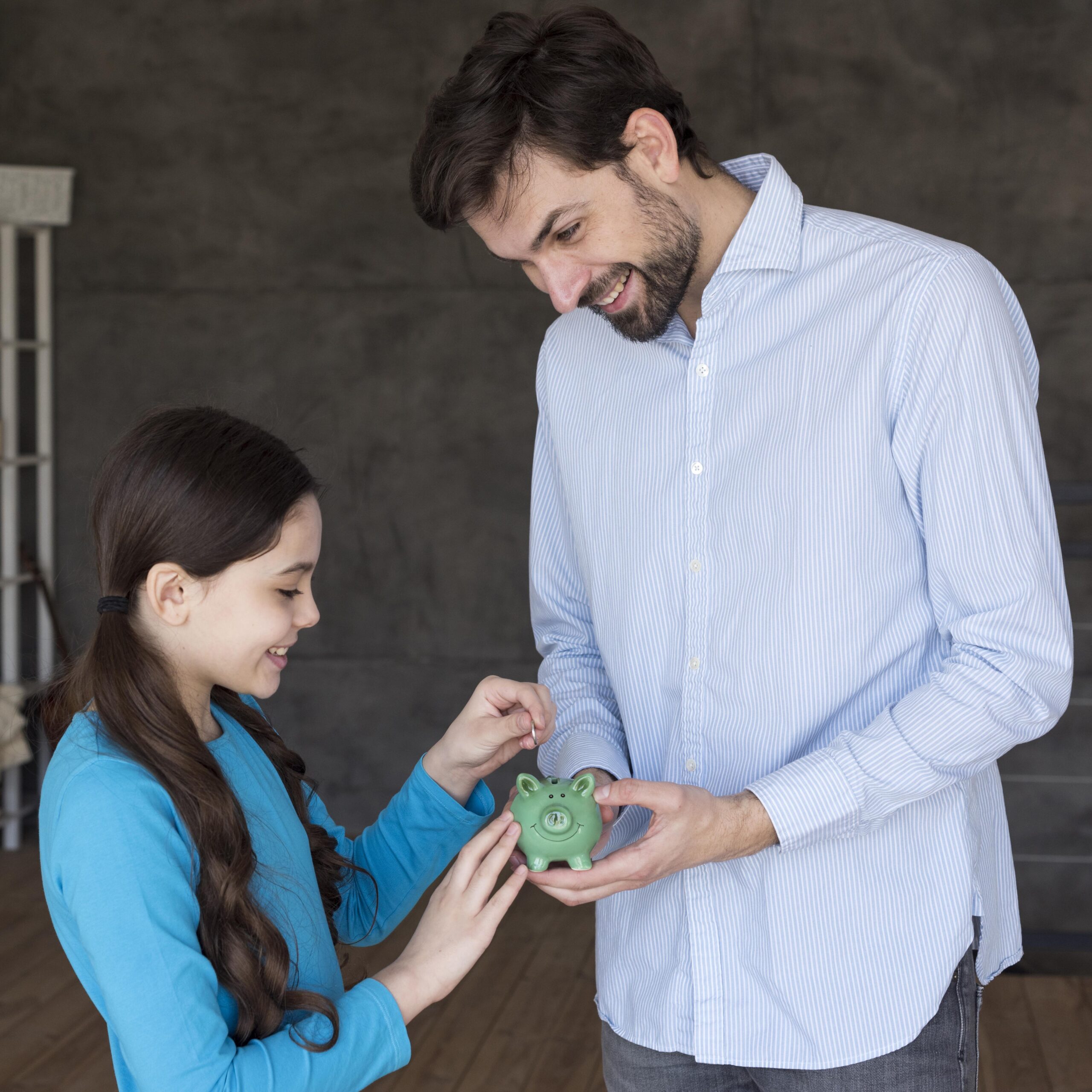
Pretend Grocery Shopping with Fake Coins and Notes: 12 Smart Ways to Teach Kids Money Management Skills
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes represents one of the most effective methods for teaching children essential financial literacy skills from an early age. This comprehensive guide explores how parents can use simple role-playing activities to build strong money management foundations while making learning about finances engaging and practical for young minds.
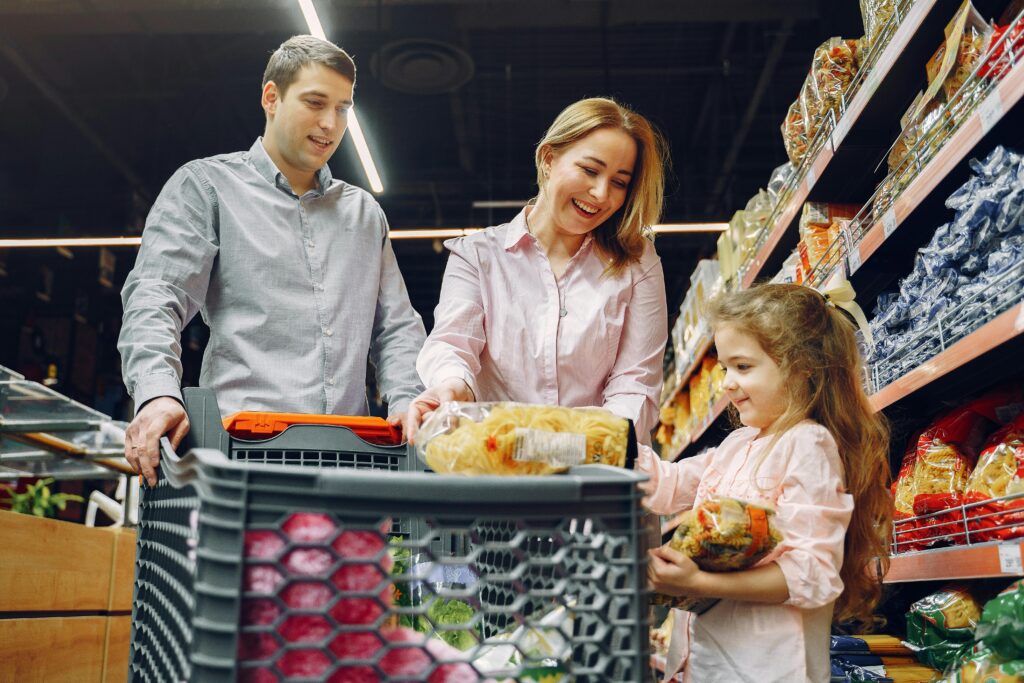

Why Pretend Grocery Shopping with Fake Coins and Notes Works for Financial Education
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes creates authentic learning experiences that mirror real-world financial decisions. According to the Reserve Bank of India, early financial education significantly improves long-term money management behaviors and economic decision-making capabilities in adulthood.
Teaching kids money management through hands-on activities helps them understand abstract financial concepts through concrete experiences. Children learn to recognize different currency denominations, practice basic arithmetic, and develop budgeting awareness through interactive play scenarios.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) emphasizes that financial literacy education starting in childhood creates more informed investors and financially responsible adults, supporting broader economic stability and growth.
“Early exposure to money concepts through play-based learning establishes positive financial habits and confidence in handling money throughout life.”
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pretend Grocery Shopping with Fake Coins and Notes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Practical Learning: Teaches real-world money skills through hands-on experience | Time Investment: Requires significant setup and supervision time from parents |
| Mathematical Skills: Develops counting, addition, subtraction, and basic arithmetic | Material Costs: Need to purchase or create fake currency and shopping props |
| Budgeting Awareness: Introduces concept of spending limits and financial planning | Limited Realism: Fake money may not convey true value of earning money |
| Decision Making: Teaches cost comparison and smart purchasing choices | Storage Requirements: Play materials need organized storage space |
| Currency Recognition: Familiarizes children with different denominations and notes | Maintenance Needed: Play money and props require replacement over time |
| Social Skills: Develops communication and negotiation abilities through role-play | Age Limitations: Very young children may not grasp abstract money concepts |
| Family Bonding: Creates shared learning experiences and quality time together | Complexity Management: Balancing educational value with age-appropriate fun |
| Confidence Building: Builds comfort and familiarity with handling money transactions | Real-World Gap: May create disconnect between play money and actual financial responsibility |
Essential Materials for Pretend Grocery Shopping with Fake Coins and Notes
Creating effective pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes experiences requires careful material selection. Start with realistic-looking play money that includes various denominations of coins and notes, helping children recognize different currency values and practice making change.
Gather empty food containers, toy groceries, or create cardboard products with price tags attached. Include shopping baskets, a toy cash register, and calculator to simulate authentic shopping experiences. The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution provides consumer education resources that can inform your product selection and pricing scenarios.
Essential financial education props include shopping lists with budget limits, price comparison charts, and simple receipt templates. These materials reinforce practical money management concepts while maintaining engaging play experiences.
“Realistic play materials create authentic learning environments that effectively bridge the gap between abstract financial concepts and practical money skills.”
Setting Up Your Home Grocery Store for Financial Learning
Transform your living space into an educational pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes environment. Designate specific areas for different product categories, mimicking real grocery store layouts with clear price displays and organized shelving systems.
Create realistic price tags using current market prices to provide authentic learning experiences. Include both regular prices and sale prices to teach comparison shopping and bargain recognition skills. The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) provides consumer price data that can inform your pricing decisions for educational accuracy.
Establish a checkout area with a cash register, receipt printer, and bagging station to complete the authentic shopping experience. This setup reinforces the entire transaction process from selection to payment completion.
“Realistic shopping environments enhance learning by providing authentic contexts for practicing financial decision-making and money management skills.”
Age-Appropriate Financial Concepts for Pretend Shopping
Different age groups benefit from specific financial concepts during pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities. Toddlers aged 2-3 can focus on coin and note recognition, simple counting, and understanding that money is exchanged for goods and services.
Preschoolers aged 4-5 can handle basic addition and subtraction, understand the concept of making change, and begin learning about budgeting through spending limits during shopping activities.
School-age children can engage with more complex concepts including percentage calculations for discounts, comparison shopping strategies, and understanding unit prices for better value decisions. The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) provides age-appropriate mathematics curricula that align with these financial learning objectives.
Advanced concepts for older children include calculating sales tax, understanding receipt details, and learning about different payment methods including cash, credit, and digital payments.
“Age-appropriate financial education ensures optimal learning outcomes while building confidence through achievable challenges and progressive skill development.”
Teaching Budgeting Through Pretend Grocery Shopping with Fake Coins and Notes
Budgeting represents one of the most crucial financial skills children can learn through pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities. Start by giving children specific amounts of play money and challenging them to purchase required items within their budget constraints.
Create shopping lists with both needs and wants, teaching children to prioritize essential purchases before spending on discretionary items. This practice mirrors real-world budgeting decisions and helps develop critical thinking about spending choices.
The Ministry of Finance, Government of India emphasizes that early budgeting education contributes to national economic stability by creating financially responsible citizens who make informed spending decisions throughout their lives.
Introduce concepts like emergency funds by having children set aside a portion of their play money before shopping, teaching the importance of financial preparation and planning for unexpected expenses.
“Budgeting practice through play activities develops financial discipline and decision-making skills that benefit children throughout their lives.”
Mathematical Skills Development Through Shopping Activities
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes naturally reinforces mathematical concepts in practical contexts. Children practice addition when calculating total purchases, subtraction when determining change, and multiplication when buying multiple quantities of items.
Introduce percentage calculations through discount scenarios, teaching children to calculate sale prices and understand the value of promotional offers. These skills directly translate to real-world shopping competency and financial awareness.
Create scenarios requiring estimation skills, such as approximating total costs before reaching checkout or determining whether they have sufficient money for desired purchases. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) includes these practical mathematics applications in their financial literacy curriculum recommendations.
Advanced mathematical concepts can include calculating unit prices to compare value across different package sizes, understanding interest concepts through layaway scenarios, or exploring currency conversion for international product comparisons.
“Mathematical skills developed through practical shopping activities create stronger number sense and computational abilities while building financial confidence.”
Teaching Smart Shopping and Consumer Awareness
Smart shopping skills developed through pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes prepare children for lifelong financial success. Teach comparison shopping by presenting similar products at different prices, helping children understand value assessment and decision-making processes.
Introduce concepts like generic versus brand-name products, seasonal pricing variations, and bulk purchasing advantages. These lessons develop critical thinking about marketing influences and value determination skills.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) provides quality standards information that can be adapted into age-appropriate discussions about product quality, safety considerations, and value for money assessments during pretend shopping activities.
Create scenarios involving limited-time offers, clearance sales, and loyalty programs to teach children about marketing strategies while helping them develop resistance to impulse purchasing and emotional spending decisions.
“Smart shopping education protects consumers from marketing manipulation while developing analytical skills for making informed purchasing decisions.”
Digital Payment Integration in Pretend Shopping
Modern pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities should include digital payment education to prepare children for evolving financial landscapes. Introduce concepts like debit cards, credit cards, and mobile payment systems through age-appropriate role-playing scenarios.
Create simple explanations about how digital payments work, emphasizing that money still comes from bank accounts or must be repaid, maintaining understanding of financial reality behind convenient payment methods.
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) promotes digital payment literacy as essential for economic participation in modern India, making this education increasingly relevant for children’s future financial success.
Discuss security concepts like PIN protection, safe online shopping practices, and understanding receipt verification, building awareness of digital financial safety from an early age.
“Digital payment education ensures children develop comprehensive financial literacy skills relevant to modern economic participation and technological advancement.”
Building Emergency Fund Concepts Through Play
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities provide excellent opportunities to introduce emergency fund concepts. Before each shopping session, have children allocate a portion of their play money to an “emergency fund” that cannot be spent during regular shopping.
Create unexpected scenarios during play, such as needing extra money for a forgotten essential item or taking advantage of a limited-time discount, demonstrating how emergency funds provide financial flexibility and security.
Teach children that emergency funds should only be used for genuine emergencies or exceptional opportunities, not for impulse purchases or wants versus needs situations.
“Emergency fund education through play activities establishes financial security habits that protect against future economic uncertainties and unexpected expenses.”
Family Financial Discussions During Shopping Play
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes creates natural opportunities for family financial discussions. Use shopping scenarios to discuss family budgeting processes, explaining how real families make spending decisions and prioritize purchases.
Share age-appropriate information about family financial goals, such as saving for vacations, education expenses, or major purchases, helping children understand long-term financial planning concepts.
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) emphasizes that family financial discussions improve financial literacy outcomes and create more informed decision-makers across generations.
Encourage children to ask questions about money, spending, and saving during play activities, creating open communication about financial topics that continues into their adult lives.
“Family financial discussions during play activities create transparent communication about money while building trust and understanding of financial responsibility.”
Creating Receipt Reading and Record Keeping Skills
Introduce receipt analysis during pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities to teach children about transaction verification and financial record keeping. Create detailed receipts for shopping activities, including item names, prices, taxes, and totals.
Teach children to check receipts against purchases, verifying accuracy and understanding each component of the transaction summary. This skill prevents overcharging and builds attention to detail in financial matters.
Create simple expense tracking sheets where children record their purchases, remaining money, and spending patterns, introducing basic personal finance management concepts through hands-on practice.
“Receipt reading and record keeping skills develop attention to detail and financial awareness that protects against errors and supports budgeting success.”
Incorporating Investment Concepts Through Advanced Shopping Play
Advanced pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities can introduce basic investment concepts appropriate for older children. Create scenarios where children can choose between spending all their money immediately or saving portions for future shopping sessions with “interest” rewards.
Introduce concepts like buying in bulk for long-term savings, seasonal purchasing strategies, and understanding how delayed gratification can lead to better financial outcomes over time.
The Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI) promotes early investment education as crucial for long-term wealth building and economic security, making these concepts valuable additions to financial play activities.
Create simple compound interest demonstrations by offering bonus play money for children who save consistently over multiple shopping sessions, illustrating how money can grow through patient financial behavior.
“Investment education through play activities builds understanding of long-term financial growth and the benefits of patient, disciplined money management.”
Safety and Security Education During Shopping Play
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities should include age-appropriate safety and security education. Teach children about protecting their money, recognizing counterfeit currency features, and understanding basic fraud prevention concepts.
Create scenarios involving lost money, stolen wallets, or suspicious offers to help children develop awareness and response strategies for financial security challenges they might encounter in real life.
Discuss the importance of keeping financial information private, not sharing PIN numbers or passwords, and being cautious about money-related interactions with strangers.
“Financial security education protects children from fraud and theft while building awareness of money safety practices for lifelong financial protection.”
Measuring Progress and Learning Outcomes
Track children’s financial literacy development through pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes activities using simple assessment methods. Observe their decision-making processes, mathematical accuracy, and understanding of financial concepts during shopping sessions.
Create progress charts showing improvement in areas like calculation speed, budgeting accuracy, smart shopping decisions, and financial vocabulary development, celebrating achievements to maintain motivation and engagement.
Document learning milestones and challenges to adapt activities appropriately, ensuring continued educational value as children develop more sophisticated financial understanding and capabilities.
“Progress tracking ensures optimal learning outcomes while maintaining engagement through appropriate challenges and recognition of achievement.”
Frequently Asked Questions
At what age should children start pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes?
Children can begin simple money recognition activities as early as age 2, with more complex budgeting and calculation concepts introduced progressively as mathematical and cognitive abilities develop through elementary school years.
How much fake money should I give children for shopping activities?
Start with small, manageable amounts that allow for successful purchases while requiring some decision-making. Gradually increase amounts as children demonstrate competency with budgeting and calculation skills.
Can pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes replace real financial education?
While excellent for building foundational skills, pretend shopping should supplement rather than replace comprehensive financial education including real-world money experiences appropriate to the child’s age and maturity level.
How do I make shopping activities educational without being boring?
Focus on fun scenarios, friendly competition, and achievement recognition while naturally incorporating learning objectives. Allow children to lead some activities and make age-appropriate choices about shopping themes and challenges.
What if my child struggles with the mathematical concepts?
Simplify activities to match current ability levels, use visual aids and concrete examples, and celebrate small improvements. Consider consulting educational resources or professionals for children with specific learning challenges.
How can I connect shopping play to real family finances?
Share age-appropriate information about family budgeting, involve children in actual shopping decisions when appropriate, and use play scenarios to discuss real financial concepts and family values about money management.
Should I correct mistakes during shopping play?
Use mistakes as teaching opportunities rather than criticism, guiding children toward correct solutions through questions and hints. Focus on learning and improvement rather than perfect performance.
How often should we do shopping activities for optimal learning?
Regular but not excessive frequency works best – perhaps weekly sessions with occasional shorter review activities. Maintain balance between financial education and other important childhood experiences and learning areas.
Pretend grocery shopping with fake coins and notes provides powerful financial education opportunities that prepare children for lifelong money management success. These activities build mathematical skills, decision-making abilities, and financial confidence through engaging, practical learning experiences.
For more financial education resources and money management guidance, explore our comprehensive blog featuring expert insights and practical financial advice. Need personalized financial education planning for your family? Contact our financial advisors for professional guidance tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Disclaimer: This article provides educational guidance for teaching financial literacy skills to children. While these activities build important money management foundations, they should supplement comprehensive financial education including real-world money experiences appropriate to each child’s developmental stage. For professional financial planning advice, consult qualified financial advisors who can provide personalized guidance based on your family’s specific circumstances and goals.
Ready to start your family’s financial education journey? Contact our certified financial planners for expert guidance on age-appropriate financial education strategies and comprehensive family financial planning services.













